Understanding the Internet of Things
Quick Links: History of IoT | IoT Today | Implementing IoT | Integration of IoT | Contact Us
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a phrase frequently mentioned in reference to our digital world. But many people don’t completely understand its function and potential impact on our businesses, economy and society.
The IoT is essentially a large network of related computing devices, sensors, machines and other objects. These objects talk to one another — collecting, sending and receiving data from one another — largely without human interaction. This means that manual labor isn’t needed to collect, send or process data — something that previously required human interaction to do. The “things” in the IoT can be any device with the ability to collect and send data through a network.
The term “Internet of Things” wasn’t coined until 1999. But in reality, the IoT has been around for many years. Even the simplest systems where data is collected through a device, then sent to a host, has contributed to the “infrastructure” of the modern IoT.
For example, in the early 1980s, a Coca-Cola machine at Carnegie-Mellon University was programmed so users could log onto the internet to check the status of the machine and see whether drinks were available. Essentially, IoT has helped join operational technology with information technology — data can be collected based on operations, analyzed with IT, then used to drive improvements in business operations.
Today, IoT technology is beginning to be used in practically every industry, from manufacturing and food and beverage, from healthcare and energy management and from transportation to agriculture. Sensors can essentially be assigned to almost everything. But as the utilization of IoT increases, it raises concern about data security and privacy.
Read on for more information on the IoT and an explanation of how it can be used to help your business.
The History of IoT and Industry 4.0
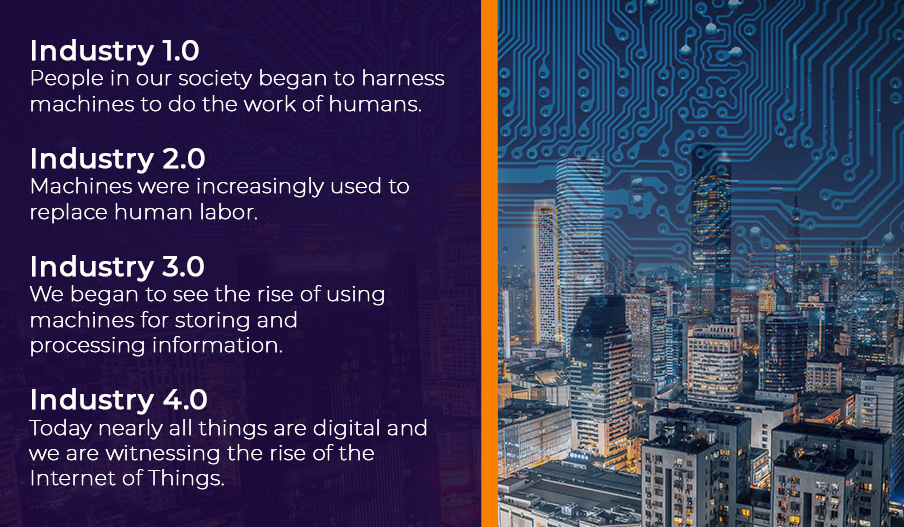
Simply put, IoT is a network of sensors and devices that collect data, then send the data to a hosted service. But IoT is also known by the name “Industry 4.0”. This name is meant to describe the major changes or “versions” the technological industry has gone through in past years. Like a version of a software or system, our technological world has experienced some major changes and updates over time:
- In Industry 1.0, people in our society began to harness machines to do the work of humans. James Watt invented the Watt steam engine, which improved upon the design and function of the existing Newcomen steam engine. With Watt’s improvements, the steam engine could now be used to power many different tasks that previously required manual labor. Watt’s work on the steam engine was so revolutionary that we named the basic unit of power, the watt, after him.
- With Industry 2.0, machines were increasingly used to replace human labor. Henry Ford created the assembly line for auto manufacturing, which allowed cars to be produced more quickly, cheaply and in mass, without requiring extensive manual labor.
- In Industry 3.0, we began to see the rise of using machines for storing and processing information. Records started to be stored digitally and computers were used to carry out complex calculations, diagnostics and other operations. Previously, this was thought to be work only humans could successfully carry out.
- Today, we have Industry 4.0, where nearly all things are digital and we are witnessing the rise of the Internet of Things. Like in prior phases, machines are performing tasks previously carried out by humans, like data collection. But now they’re also controlling and interacting with one another without any human guidance or intervention.
IoT opens the possibilities of a new era of data collection and data science. It can collect sensor data from a large, disperse set of sources on a scale that would be impossible if left to human labor — then make intelligent decisions based on the data and deliver relevant, real-time notifications as needed.
Weighing solutions are an obvious place to start with integrating IoT technologies into a wide variety of modern industries. Plus, monitoring production levels at various points throughout a meat production plant or studying real-time data for tanks of liquid ingredients in blending and batching operations can help tip you off about problems before they slow you down. Here are some additional practical examples of IoT at work in the real world:
- IoT can be used to track inventory within a manufacturing or food processing plant. When a product gets low, a notification can be sent to management to reorder. Alternatively, your IoT setup could automatically reorder products once levels fall below a decided-upon limit.
- IoT can also keep forklift operators and other personnel appraised on where to go next. Notifications can include all the necessary details to keep them moving, such as when a production line has filled a pallet and it needs to be picked up and moved onto a truck. Rather than driving around or waiting for a call, the driver can see production points and know where to go next to keep the production process moving fluidly.
Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things is likely just another stop along the path of our industry’s transformation. But it’s clearly a big driving force. Experts predict that IoT could have an economic impact of $11 trillion by 2025 and influence almost the entire global economy by 2025.
So what has caused the rise of Industry 4.0? The answer lies in the evolution of technology. Unlike in Industry 1.0 and 2.0, use of technology has become an essential part of our everyday lives. With technology becoming so central in our world, it’s also become more accessible and affordable. So this has changed how we use technology. Sending and processing data has become more cost-effective. Sensors have become half the price they were previously.
With technology so pervasive in the world marketplace, IoT has emerged as a way for businesses to improve their operations, conserve resources and increase their efficiency.
IoT Today
Companies are beginning to look at IoT as a way to do business more effectively. By 2020, global spending on IoT is estimated to reach $1.29 trillion with a compound annual growth rate of 15.6 percent.
The biggest area of spending will be for hardware: the sensors and modules that collect data and send it to the network. By 2020, spending on IoT hardware will reach approximately $400 billion. Additional spending will be needed for software, power and connectivity.
Security will also be a key concern related to IoT. Businesses will want to ensure that data is collected and analyzed securely and that systems are monitored to avoid potential intrusions. With more data being collected, IoT systems can easily become a target for criminals looking to steal data.
Implementing IoT
IoT solution implementation requires careful planning to ensure that the solution is implemented in a way that will most benefit the business. We encourage you to work with the thoughtful application specialists at Precision Solutions to find the ideal setup and equipment for your IoT ambitions and for the specific nature of your business operations.
For IoT to be implemented successfully, businesses should consider the following factors:
1. Sensors
Sensors have become more affordable and effective over the past few years. Today’s sensors allow us to measure new elements and collect more data than ever before, and with far greater accuracy. Today’s sensors can collect data on everything from temperature, moisture and air pressure to vibration, light levels and physical position.
Sensor accuracy is typically within one or two percent. Most sensors can also be easily integrated with other IT systems and networks so data can be collected and processed. Typically, sensors are easily mounted with a clip-on, screw-on or adhesive attachment.
So, for choosing the sensors for your IoT system, there are many options. Consider what data you’re looking to collect. This can help you select the right sensor type for your needs.
2. Connectivity
Sensors in an IoT system have to be able to connect to and communicate with the Internet. There is a wide variety of technologies that exist that can help connect sensors to the Internet, involving both wired, wireless and combination setups.
The ideal connectivity setup will depend on the environments where the sensors are collecting data. Will your sensors be outdoors or exposed to weather conditions? This means they’ll need to be able to stand up to fluctuating temperatures, moisture levels and other weather elements.
The location of the sensors can also affect whether the sensors can be wired or will need to communicate wirelessly. Also, consider the speed you need from your connection. How quickly do you need your sensors to send data to the Internet?
All of these factors — environment, location, speed needs and more — should be taken into account when determining your ideal connectivity setup.
3. Security
With large amounts of data being collected and sent between sensors and the Internet, security is a key part of a successful IoT solution. Sensors that are part of an IoT network will be constantly sending, and potentially receiving, large amounts of data. With all this available data, data security cannot be overlooked.
Companies should consider what data security measures are appropriate for keeping their data secure, including VPNs and firewalls. In all cases, sensors and other devices should be encrypted before they’re connected to the Internet. Otherwise, anyone can access the data being sent.
With IoT growing in popularity and cyberattacks on the rise, it’s critical to keep security at the forefront when designing IoT solutions.
4. Data Collection
Sensors in an IoT network are collecting and sending large amounts of data. So, once the data is collected and aggregated, companies need to make decisions on how much data to store and for how long.
This decision largely depends on the goals of the data collection. Are you collecting data to look at long-term trends? In this case, you will want to collect and archive data for a longer, pre-defined period so you can look at trends in the data over a longer period of time. If you’re continuously analyzing data, it’s less important to archive data over the long run.
And your data collection decisions can be flexible over time if needs change. For example, if you’re monitoring a machine for fluctuations in run-time and several months go by without any major changes, you can begin archiving and deleting that data. But if the machine has multiple run-time changes within a month, data should continue to be collected and saved so business owners can analyze possible reasons for outages.
The success of an IoT solution’s return on investment is largely dependent on how the data is used. While it’s great to collect data, the data doesn’t mean anything to a business unless it’s utilized. All businesses should take the time to set goals for data collection before investing in an IoT solution. This will ensure your new IoT solution gives you valuable feedback and isn’t just a fancy piece of IT.
5. Making Decisions With Data
Once you have your IoT system up and running, it’s time to look at the trends and make decisions about your business and processes based on the feedback you’re receiving. You might realize you’re not collecting a critical variable you should be. Or maybe you’re collecting data that’s not giving you the information you really need. If you change your process based on trends in your data, you may need to change your data collection process to account for the changes.
You can also use the data you’re collecting for making decisions about your business and assets. For example, in machinery, you can monitor environmental exposure, run-times, temperature and corrosion rate to determine when the machinery should be replaced or brought in for maintenance.
For a practical example of how Precision Solutions can help out, consider the benefits of monitoring production levels. If industry standards show a product line can handle 20 boxes each hour but recent data collection shows you’re only achieving 16, management can start looking into personnel issues, equipment failures or product waste levels — all of which are connected through IoT — to determine the problem and then take corrective action.
When used to their fullest potential, IoT systems are used to analyze data, monitor systems and correct issues. For example, if a network of IoT sensors was deployed to monitor an office building, the system could make decisions on power usage based on building occupancy and status. The system could monitor when rooms are occupied and turn on lights and fans accordingly. If more people enter a room, increasing the temperature of the room with added body temperature, the system could turn on air conditioning or increase fan speeds to circulate air faster.
And in the event of an emergency, like a fire, the system could notify emergency services, sense whether all people have left the building and seal fire doors and cut off air flow to the rooms with the fire.
When thinking about different decisions, business owners should consider all possible scenarios and outcomes and then design the business rules of their system accordingly.
Why Integration Is Critical to IoT Success
Without effective integration, IoT solutions can’t achieve real success.
Often, not enough attention is paid to integrating a new IoT solution. According to Benoit Lheureux, a vice president at research firm Gartner, organizations implementing IoT solutions often underestimate how complex integrating IoT is and overestimate the built-in integration capabilities of their IoT platforms.
Gartner predicts that through 2018, at least half the cost of implementing an IoT solution will be spent on making sure IoT components are properly integrated with existing systems. It’s important that organizations plan integration thoroughly and carefully define all integration requirements.
In almost all cases, it’s best for companies to keep the initial scope of the project small. This will allow your company to test the waters and pick-up some quick benefits, and then have a better idea how and where you will get the best benefit for additional investments. Over time, as the project matures and integration requirements grow, you can bring in new integration solutions and technologies.
When planning for a successful integration, organizations should consider the following:
1.Potential Integration Challenges
It’s important to consider what sort of fundamental challenges exist that can affect integration. Usually, these challenges involve the devices and applications used to collect the data, the data being collected and the processes involved with collecting the data. IoT platforms must be able to connect and receive data from all connected devices and then integrate data sent from each device and trigger business rules as needed.
2. Challenges Related to Scope
Projects become more complicated and challenging when the scope expands, so it’s important to carefully plan for any increases to your scope of integration. This can include anything from additional applications, IT assets or ecosystems. If your system is being linked to an additional source, it will have to integrate additional data.
3.Existing Integration Skills
Most businesses aren’t used to integrating the amount of data an IoT system brings in. IoT systems — even the simplest ones — produce a constant flow of data that must be processed and integrated. With this amount of information flowing in, organizations have to evaluate their existing skills with data integration and then consider whether new integration capabilities or data management resources need to be sought out in order to successfully integrate IoT data.
Using IoT on an Industrial Scale
There is great potential in IoT solutions to influence industries across the market. However, IoT devices require proper integration to be effective. With the help of IoT experts, businesses can integrate their IoT devices and ensure they are used in the most effective and efficient manner.
For businesses looking to integrate IoT equipment, technologies and software into coordinated systems, Precision Solutions provides the expertise needed to help you integrate your system and keep your operations running smoothly. We offer industrial smart scales for warehouse and manufacturing customers. Through our Integrated Solutions Group, we provide scale integration services to help your company overcome integration challenges.
With Precision Solutions, you’ll experience a high level of service delivered through our renowned Benchmark Customer Care. Our staff will work with yours to design, develop and implement the best scale software solution for your company. Our services and solutions will ensure that your weighing, measurement and compliance processes are efficient and effective.
Precision Solutions offers integration for scales and barcoding solutions to companies in the Lehigh and Delaware Valley regions of Pennsylvania as well as throughout the state of New Jersey. To learn more about us and start getting the most out of your business software today, contact Precision Solutions.